
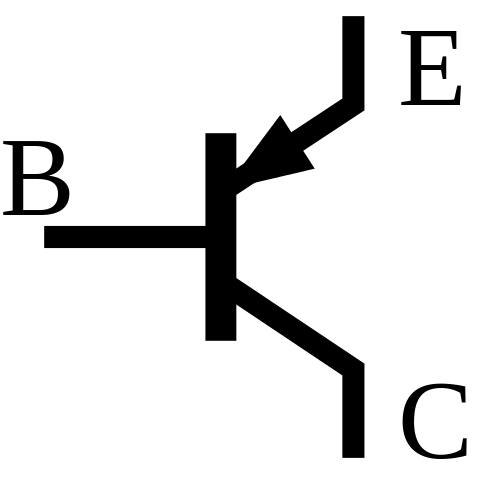
Basic transistor symbol is shown without the arrow (inward and outgoing). The symbols of NPN and PNP transistors are shown distinctly. Transistor Symbols:įor the sake of convenience, the transistors are represented below by a schematic diagram. But before that, you must know about the symbolic representation of PNP and NPN transistors. The whole thing will be clear once you read about the transistor working in this post. As shown in the figure above, the collector of the PNP transistor is reverse biased and receives hole charges that flow in the outer circuit while the collector of NPN transistor receives electron charges. The collector is always reverse biased and its function is to remove charges from its junction with the base.
(iii) Collector: It is a moderately doped terminal which basically collects electron. The Depletion layer is formed in the base junction of the transistor. The base-emitter junction is forward biased and allows low resistance to the emitter circuit while the base-collector junction is reverse biased and provides high resistance in the collector circuit. (ii) Base: It is lightly doped terminal through which electrons pass from the emitter to collector. As shown in the figure above, the emitter of PNP transistor (right side figure) is forward biased and supplies hole charges to its junction with the base while the emitter of NPN transistor (left side figure) supplies electron charges to its junction. base so that it can supply a large number of majority carriers. (i) Emitter: It is a heavily doped terminal through which electrons enter. The 3 terminals of the transistor are explained briefly: The Middle portion is known as the base which forms two junctions between the emitter and the collector as shown in the figure.
The portion on one side is the emitter and the portion on the opposite side is the collector. Transistors comprise of three sections of doped semiconductors. A transistor is a combination of two p-n junction, that’s why it is considered as a combination of two diodes connected back to back.ĭarlington Transistor Transistor Terminals:.Most important factor in the function of a transistor is the middle section which is present as a very thin layer.In each type of the transistor, the following points may be noted: Sponsored Links Block diagram of NPN transistor Look for the image below for its basic block diagram. The basic block diagram of PNP transistor is shown in the image below: Block diagram of PNP transistor (ii) NPN Transistor:Īs the Name suggests, in this type of transistor, p-type semiconductor piece is sandwiched between two pieces of n-type semiconductor layers. In this type of transistor, n-type semiconductor piece is sandwiched between two pieces of p-type semiconductor layers. The process of sandwiching is called fabrication of transistor.ĭepending on the way of construction of transistor, it is of two types: (i) PNP Transistor: Different types of Transistors: Pictorial form Transistor construction:Ī Transistor is a three layer semiconductor device in which one type of semiconductor (Either P-type or N-type) is sandwiched between two similar other types of semiconductor. In short, “Transistors are the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices basically used for controlling, amplifying and generating electrical signals.” Before going on the working and operation part, let me first tell you about its construction. Earlier we have covered its basics in the previous post of transistors where I have explained about what it is and its types. PNP transistor and NPN Transistor are one of the most asked queries by students In this post, we are going to explain transistor working and its operation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
